- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
English
Silicone rubber materials are widely used in the medical device industry. Their working principle is mainly based on their unique physical and chemical properties. The following is a detailed introduction:
Silicone is a synthetic organosiloxane polymer with good biocompatibility, high chemical stability, strong temperature resistance, excellent flexibility and elasticity, superior adsorption and controlled release properties, and good filling and support properties
Typical application examples:
1. Catheters and tubing: High-viscosity silicone rubber is often used to make catheters, while liquid silicone rubber is used to make balloons, which are filled with air after being inserted into the bladder to fix the device in place.
2. Implantable devices: The stability, non-toxicity and insolubility in body fluids of silicone make it suitable for long-term implantable devices such as pacemaker shunts and joint replacements.
3. Prostheses: Silicone is used in prosthetic devices because it can mimic the structure and flexibility of human skin and tissue, providing patients with more natural and comfortable prostheses.
4. Surgical tools and equipment: Silicone rubber is used in the handles and grips of surgical tools to provide better operation and control, and will not degrade after multiple rounds of disinfection.
5. Hearing aids: The soft and flexible properties of silicone make it an ideal choice for hearing aids, providing comfort to the user.
6. Seals, gaskets and rings: Silicone seals and gaskets are used in a variety of medical devices to ensure air-tight and liquid-tight seals.
7. Medical wearables: Silicone is used in wearable medical devices such as those that monitor walking due to its skin-friendly properties and durability.
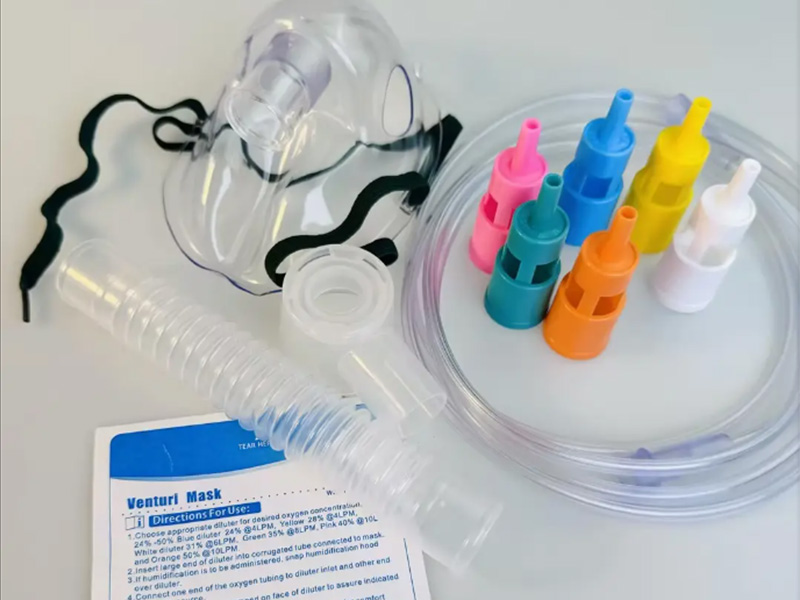
8. Respiratory masks and breathing devices: The flexibility and non-toxicity of silicone are critical for masks and devices that assist breathing.
9. Infusion pumps and valves: These devices often contain silicone components due to silicone's chemical inertness and compatibility with various drugs and solutions. In addition, valves also play a key role in delivering fluids to the body.
 |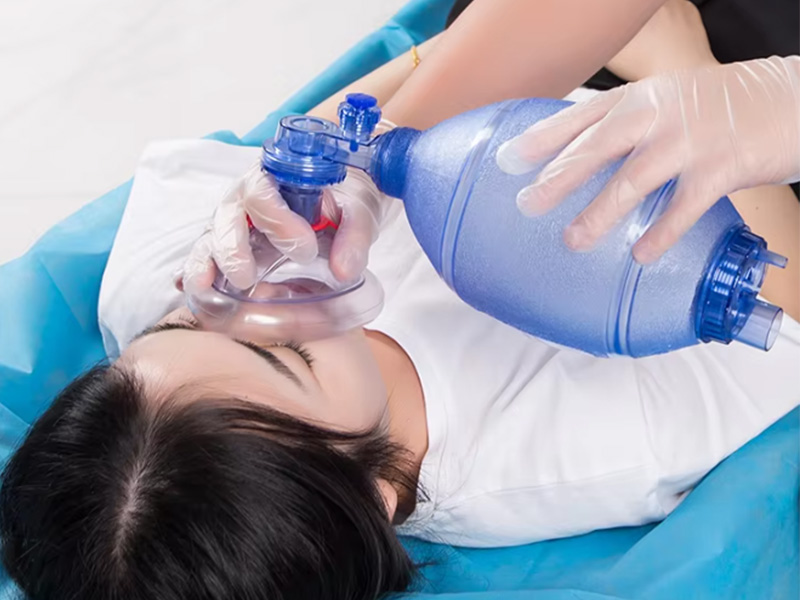  |
 |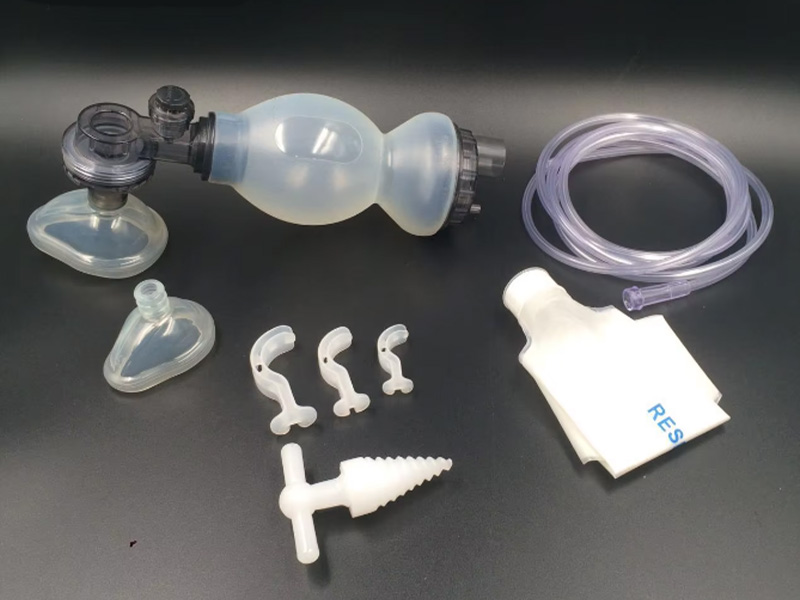  |